Translate Language
Why Thailand & Cambodia Clash: Nationalism, Temples & Unresolved Borders
A recent ceasefire paused violent border clashes between Thailand and Cambodia, but the core conflict remains unresolved. At its heart lies a bitter cultural rivalry over sacred temples and contested colonial-era borders. This complex dispute offers critical insights into nationalism, geopolitics, and colonial legacies—key themes for competitive exams.
The guns have fallen silent—for now. After days of deadly border skirmishes that killed dozens and displaced over 260,000 civilians, Thailand and Cambodia agreed to an immediate ceasefire in February 2024. But don’t mistake this truce for peace. The real conflict isn’t just about land; it’s a centuries-old cultural showdown.
Why Are They Fighting?
The Spark: Recent clashes erupted after a Thai soldier lost his leg to a landmine (Thailand blamed Cambodia). Cambodia retaliated by recalling diplomats, banning Thai TV dramas, and blocking fruit imports.
The Powder Keg: Nationalist fervor in both countries fuels tit-for-tat actions. Thailand launched airstrikes; Cambodia responded with rockets.
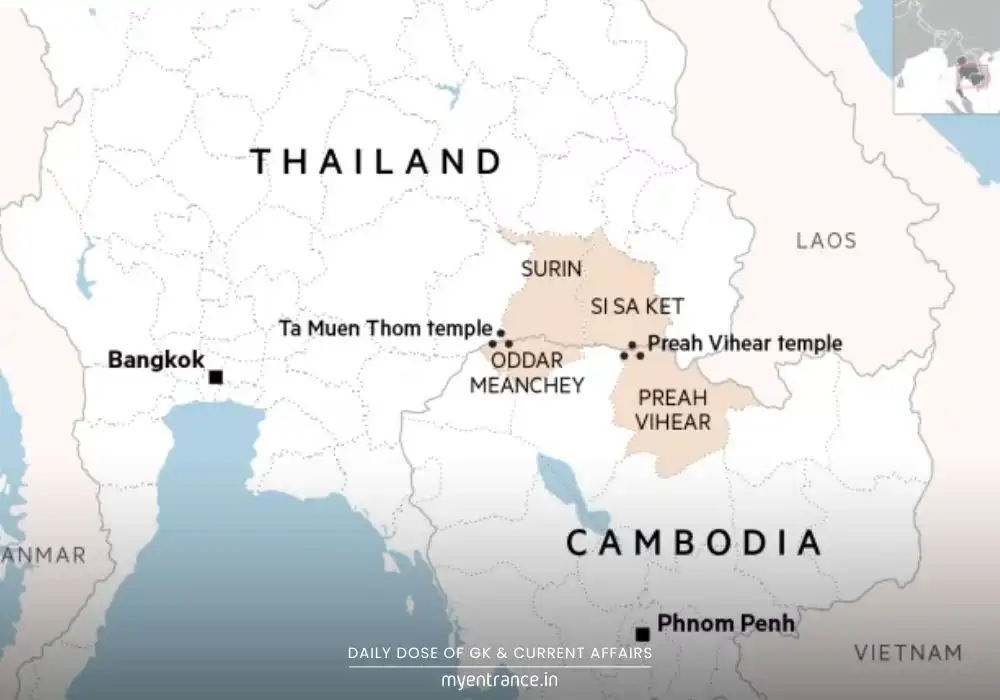
The Heart of the Conflict: Preah Vihear Temple
This 900-year-old Hindu temple, sacred to both nations, sits on a disputed border drawn by French colonizers in 1907.
In 1962, the International Court of Justice awarded it to Cambodia—but Thailand never fully accepted the ruling.
Cultural Nationalism: Both countries claim to be the “true heirs” of Khmer heritage. Governments exploit this rivalry to rally domestic support.
Bigger Than One Temple
Similar disputes surround other border temples like Ta Moan Thom, where recent fighting occurred.
Shared ethnicity, language, and Theravada Buddhism haven’t healed the rift. Instead, competing historical narratives deepen animosity.
Why the Ceasefire Might Not Last
As scholars note, Thailand and Cambodia are “prisoners of a remade past.” Until cultural ownership and colonial borders are addressed, truces will remain temporary.
Why This Matters for Exams (UPSC, PSC, KAS, SSC):
GS Paper II (Mains): Classic case study on how colonial borders and cultural nationalism trigger modern conflicts.
International Relations: Impacts ASEAN stability and India’s “Act East Policy” partnerships.
Current Affairs: Illustrates how historical disputes shape contemporary geopolitics.
Ethics/Governance: Shows how governments weaponize heritage for political gains.
Questions & Answers on Thailand-Cambodia Issues:
Q1: What triggered the 2024 Thailand-Cambodia border clashes?
A1: Immediate triggers were a landmine blast injuring a Thai soldier and retaliatory diplomatic expulsions, escalating into artillery duels and airstrikes.
Q2: Why is Preah Vihear Temple central to this dispute?
*A2: Both nations claim cultural ownership of this 11th-century temple. A 1962 ICJ ruling awarded it to Cambodia, but Thailand contests the colonial-era border it sits on.*
Q3: How does nationalism fuel this conflict?
A3: Governments in both countries promote competing historical narratives, using temple disputes to stoke patriotism and consolidate domestic support.
Q4: What role did colonialism play?
*A4: France’s 1907 border demarcation ignored ethnic/cultural ties, creating ambiguous boundaries that remain contested today.*
Q5: Why should UPSC aspirants study this conflict?
*A5: It exemplifies GS-II themes: “Effect of policies of developed/developing nations on India’s interests” and “Post-colonial border disputes.”*
Get 3 Months Free Access for SSC, PSC, NIFT & NID
Boost your exam prep!
Use offer code WELCOME28 to get 3 months free subscription. Start preparing today!















