Translate Language
KYC (Know Your Customer) – Importance, Process & Regulations for Banking & Competitive Exams
KYC (Know Your Customer) is a crucial regulatory process used by banks, financial institutions, and other regulated entities to verify customer identities. It helps prevent financial crimes like money laundering, fraud, and terrorist financing. In India, KYC compliance is governed by RBI, SEBI, and other regulatory bodies. This guide covers the KYC process, its types, e-KYC advancements, and its role in financial security—essential knowledge for banking and competitive exams.
What is KYC (Know Your Customer)?
KYC, or Know Your Customer, is a mandatory verification process that financial institutions follow to confirm the identity of their clients. It is designed to:
Prevent illegal financial activities such as money laundering, fraud, and terrorism financing.
Ensure compliance with global and national financial regulations.
Protect institutions and customers from financial crimes.
Who Regulates KYC in India?
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) – For banks and NBFCs.
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) – For stock markets and investment firms.
Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority (IRDAI) – For insurance companies.
Financial Action Task Force (FATF) – Sets international AML (Anti-Money Laundering) standards.
Key Documents Required for KYC
Identity Proof: Aadhaar, PAN, Voter ID, Passport, Driving License.
Address Proof: Utility bills, Bank statements, Rental agreement.
Photograph: Recent passport-sized photo (for physical KYC).
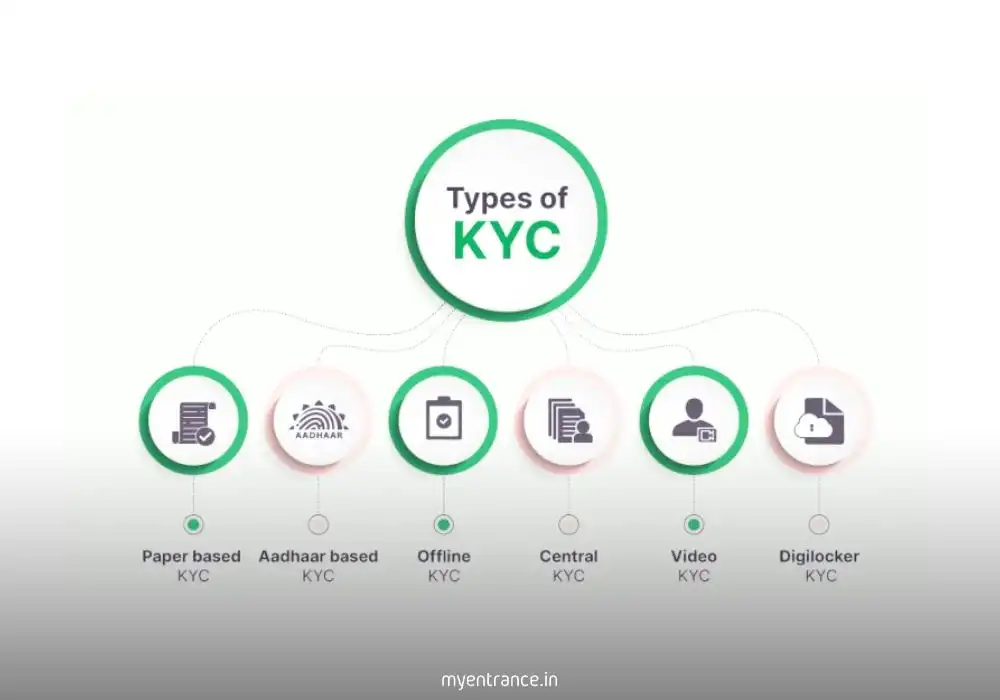
Types of KYC Processes
1. Customer Identification Process (CIP)
The first step where basic details like name, address, and ID proof are collected.
Ensures the customer is who they claim to be.
2. Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
A deeper analysis of the customer’s financial behavior.
Helps detect suspicious transactions and assess risk levels.
3. Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD)
Applied for high-risk customers (politically exposed persons, large transactions).
Requires additional verification and monitoring.
e-KYC: The Digital Revolution
With advancements in technology, e-KYC (Electronic Know Your Customer) has simplified the verification process:
Aadhaar-based e-KYC (UIDAI-authenticated) allows instant verification.
Paperless & Fast: Reduces manual paperwork and speeds up onboarding.
Secure: Uses OTP and biometric authentication for added security.
Used by: Banks, fintech companies, and mutual funds.
Note: e-KYC requires customer consent under India’s data protection laws.
Why is KYC Important for Banks & Financial Institutions?
Prevents Financial Fraud: Stops identity theft and illegal transactions.
Regulatory Compliance: Avoids heavy penalties (e.g., HSBC fined $1.9 billion for AML lapses).
Builds Trust: Ensures only genuine customers use financial services.
Global Standards: Helps institutions align with FATF guidelines.
KYC Questions for Competitive Exams (SSC, UPSC, Banking)
Q1: What is the full form of KYC?
Ans: Know Your Customer.
Q2: Which Indian authority regulates e-KYC via Aadhaar?
Ans: UIDAI (Unique Identification Authority of India).
Q3: What is the purpose of Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD)?
Ans: To conduct stricter verification for high-risk customers.
Q4: Name two documents accepted as KYC proof in India.
Ans: Aadhaar Card and PAN Card.
Q5: Which global body sets AML and KYC standards?
Ans: Financial Action Task Force (FATF).
KYC is a critical security measure in the financial sector, ensuring transparency and compliance. For competitive exam aspirants, understanding KYC norms is essential, especially for banking, SSC, and UPSC exams. Stay updated with MyEntrance.in for more exam-focused current affairs and study materials!
Get 3 Months Free Access for SSC, PSC, NIFT & NID
Boost your exam prep!
Use offer code WELCOME28 to get 3 months free subscription. Start preparing today!














