Select Language
All About ISRO: India’s Journey in Space Technology & Innovation
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is India’s national space agency, dedicated to harnessing space technology for societal and scientific benefits. Established in 1969, ISRO has achieved remarkable milestones, including lunar missions, satellite launches, and global collaborations.

ISRO: Pioneering India’s Space Ambitions
India’s journey into space began with the formation of the Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR) in 1962, under the visionary leadership of Dr. Vikram Sarabhai. Recognizing the potential of space technology, the government established ISRO on August 15, 1969, replacing INCOSPAR with a broader mission. Later, in 1972, the Department of Space (DOS) was created, bringing ISRO under its umbrella to streamline India’s space programs.
Key Objectives of ISRO
ISRO’s primary goal is to develop and utilize space technology for national progress. Some of its major contributions include:
Satellite Communication & Broadcasting: Enabling television, telemedicine, and internet services across India.
Remote Sensing & Resource Management: Monitoring agriculture, weather, and natural disasters.
Navigation & Security: Supporting defense and civilian applications with systems like NavIC.
Scientific Research: Conducting lunar, planetary, and astrophysics missions.
Major Achievements of ISRO
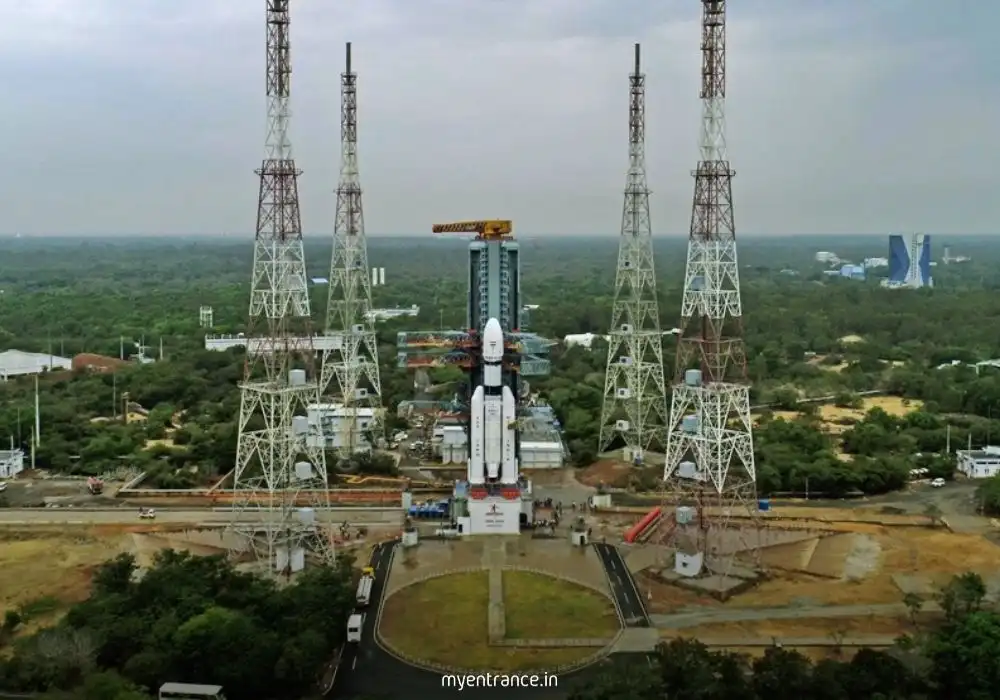
Launch Vehicle Development: ISRO built the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) and Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV), making India self-reliant in satellite launches.
Chandrayaan & Mangalyaan: India’s successful lunar and Mars missions placed ISRO among elite space agencies.
Reusable Launch Vehicle (RLV): A step towards cost-effective space travel.
Record-Breaking Satellite Launches: ISRO holds the record for launching the most satellites (104) in a single mission.
ISRO’s Major Centers & Their Roles
ISRO operates through specialized centers across India:
Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC), Thiruvananthapuram: Designs launch vehicles.
U R Rao Satellite Centre (URSC), Bengaluru: Develops satellites.
Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC), Sriharikota: Primary launch site.
Liquid Propulsion Systems Centre (LPSC): Handles propulsion technology.
Space Applications Centre (SAC), Ahmedabad: Focuses on satellite applications.
National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC), Hyderabad: Processes satellite imagery.
ISRO’s Impact on Science & Education
Beyond technology, ISRO promotes science education through:
Scholarships and research programs.
Collaborations with universities and institutions.
Public outreach initiatives to inspire young scientists.
Sample Questions & Answers About ISRO
1. When was ISRO established?
Answer: ISRO was founded on August 15, 1969, replacing INCOSPAR.
2. What was India’s first mission to Mars called?
Answer: Mangalyaan (Mars Orbiter Mission), launched in 2013.
3. Which ISRO center is responsible for satellite launches?
Answer: Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC), Sriharikota.
4. What is the full form of PSLV?
Answer: Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle.
5. Who is known as the father of the Indian space program?
Answer: Dr. Vikram Sarabhai.
Most Predicted Questions
Comprehensive study materials, Expert-guided tips & tricks, Mock tests and instant results.
Start your SSC, NIFT, NID, FDDI, PSC journey today with MyEntrance, your ultimate online coaching platform.